 English
EnglishThe test aims at logatom recognition in noise, specifically at the identification of consonants and hence at the early assessment of a high frequency hearing loss. The test is fully automated. Three alternative VCVs (e.g. aFa, aGa, aSa) are displayed on the touch screen. VCVs are presented via headphones, insert earphones or loudspeakers at different signal-to-noise ratios. The subject has to select the correct item from the screen. Recordings are available with speakers of different languages (e.g. Italian, German, English2 ) and with different character representations (e.g. Latin, Greek, Farsi, Hindi, and Cyrillic).
Two SUN workflows are available:
– SUN Predefined allows for conducting the test with pre-determined signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) groups, i.e. the test starts at a certain SNR whereupon during the test the SNR is reduced after a fixed number of words. The sequence of words is fixed and optimized with regard to the intelligibility of the VCVs. The speech level remains constant during the entire test. The test determines a score dependent on the number of correct answers (Paglialonga et al., 2011a,b).
– SUN Adaptive allows for conducting the test with an adaptive SNR (similar to Kaernbach, 1991). The speech level is decreased after a correct answer and increased after an incorrect answer. The noise level remains constant during the entire test. An additional question mark button is present which may be pressed if the subject did not understand the logatom. The test provides an SNR threshold as result.
PRACTICAL USE
Select SUN from the module selection screen. If more than one speech test is licensed, SUN can be found in the Speech section. If necessary, change the parameters (e.g. test mode, test level, masking noise type, language, character set) as required. Make sure to select a language and character set that is familiar to the tested subject.
Before starting the test, instruct the subject about the task. On the display, three different VCV options are visualized. However, a voice pronounces only one of them. The subject shall listen to a speech sample. After the speech sample is played, the subject is asked to press the button, which corresponds to the word that has been understood. If the word has not been understood the subject shall guess and press any button (SUN Predefined) or the subject may press the question mark button (SUN Adaptive) (see Figure 7). Make sure that the subject understands the task.
In order to accustom the subject to the words you may start with a training phase (Training mode needs to be enabled in settings). In the training phase, some of the logatoms from the test are played without noise. Proceed to the test phase if the subject is familiar with the task. Before starting the training or test phase, make sure that a valid transducer is connected (headphone, insert earphones or loudspeakers) and select the test ear. The training or the test starts. Please note that during the SUN Predefined test, the initial responses are not counted for the final
result.
Dependent on age and physical/mental abilities, the test may be conducted completely selfcontrolled (i.e. subject enters response) after instruction or with assistance of the examiner. Supervision by a qualified examiner is recommended at all times.

Figure 1: User interfaces for different SUN test modes (left: SUN Predefined; right: SUN Adaptive)
After the test is finished, for SUN Predefined the result is shown as a score with a traffic light status (see Figure 8 – left) or for SUN Adaptive as an SNR threshold together with a score and a traffic light status (see Figure 8 – middle/right).
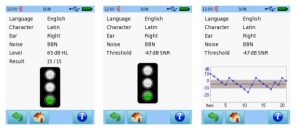
Figure 2: SUN result (left: SUN Predefined; middle: SUN Adaptive with traffic light view; right: SUN Adaptive with SNR time course view)
The time course of the SNR is additionally shown in a graph when pressing on the result screen. The three-stage status light refers to the following definitions: green for hearing ability within normal range, yellow for hearing ability which might be below normal range, red for hearing ability well below normal range. The limits between hearing range groups depend on the selected language. Please note that during this test the footer is hidden. You may activate the footer by pressing the power on/off switch briefly.
STUDY RESULTS
A study on the effectiveness of SUN (predefined mode) for adult hearing screening was performed at the Institute of Biomedical Engineering (IsIB), Milan, Italy (Paglialonga et al., 2011a). The study was conducted on 1273 adolescents and adults (13 to 89 years) with varying degrees of audiometric thresholds including SUN (predefined mode) in Italian language and pure-tone audiometry at 1, 2, and 4 kHz as reference. Tests were performed both in an environment with low and high ambient noise. After the test, all subjects were asked to fill a questionnaire for evaluating the difficulty of the task, the test duration and the overall rating. The main outcome of the study was that SUN is suited for adult hearing screening because of the following detailed findings: The overall SUN result was in
line with pure-tone audiometry with a good correlation between the three SUN categories (traffic light status) and three specifically defined PTA classes. The test performance was similar across all subjects independent of age. The test performance was also not influenced by ambient noise levels up to 65 dB(A) so that the test may also be performed in a non-clinical setting, where ambient noise is not typically controlled (e.g. hearing aid providers). The test time was very short with two minutes on average for both ears. Even older adults typically managed to conduct the test within one minute per ear. This is deemed as an important factor for a hearing screening test because inattentiveness and fatigue are likely to increase with increasing test time. The cognitive load was low and the
acceptance of the test was very high. About 85 % of the subjects considered the test to be easy or slightly difficult. 95 % of the subjects judged the test duration to be short or fair. More than 90 % of the subjects rated SUN pleasant or neutral.
A further study (Paglialonga et al., 2013) extended the above data by testing SUN (predefined mode) in more than 6000 subjects. SUN was found to be very reliable with a good correlation to pure-tone audiometry and self-reported hearing handicap. The test’s sensitivity and specificity to identify disabling hearing impairment were 84 % and 75 %, respectively. Test time was on average lower than 1 minute per ear.

 Українська
Українська Русский
Русский